
Student Handbook |
FMST 0411
17 Dec 99
TERMINAL
LEARNING OBJECTIVE:
1. Given a casualty with a tension pneumothorax in a combat environment (day and night) and
the standard Field Medical Service Technician supplies and equipment, perform a needle
thoracentesis, per the reference. (FMST.04.12)
ENABLING
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
1. Without the aid of reference materials, identify the anatomical landmarks of the chest related to the insertion of a catheter for needle thoracentesis, per the student handout. (FMST.04.12a)
2. Without the aid of reference materials and given a list, identify the purpose and indications for a needle thoracentesis, per the student handbook. (FMST.04.12b)
3. Without the aid of reference materials and given a list, select the correct procedural sequence for the performance of a needle thoracentesis, per the student handbook (FMST.04.12c)
4. Without the aid of reference materials and given a list, select the proper equipment needed for performing a needle thoracentesis, per the student handbook (FMST.04.12d)
5. Without the aid of references and given a FMST MOLLE Medic bag and a simulated casualty, perform a needle thoracentesis, per the student handbook. (FMST.04.12e)
OUTLINE:
A. NEEDLE THORACENTESIS
1. DEFINITION: The introduction of a needle or catheter into the pleural space to release trapped/accumulated air within the pleural space.
2. This procedure is used to decompress the pleural cavity and allow the collapsed lung to re-inflate. This procedure also reduces the pressure on the heart and unaffected lung usually associated with a tension pneumothorax. The procedure is to be performed on rapidly deteriorating patients who have developed a tension pneumothorax. (If this technique is used and the patient does not have a tension pneumothorax, there is a 10% to 20% risk of producing a pneumothorax and or causing damage to the lung.)
b.
Indications FOR NEEDLE THORACENTESIS:
1.
Tension Pneumothorax:
a. Can occur from either blunt or penetrating trauma.
1. Air enters the pleural cavity on inspiration but is prevented from escaping on exhalation.
2. Eventually the lung on the affected side completely collapses.
3. As the air pocket increases with each breath, it will eventually grow large enough to start pressing against other internal structures within the chest cavity, predominantly the trachea, heart, and great vessels.
4. This additional pressure is responsible for the life threatening complications seen with this condition.
b. Signs and Symptoms:
1. Dyspnea - labored breathing
2. Anxiety
3. Tachypnea rapid and shallow breathing
4. Diminished or absent breath sounds on the affected side
5. Hypotension
6. Distended neck veins
7. Tracheal deviation
Note:
Tracheal deviation is a late finding and its absence does not rule out a
Tension Pneumothorax.

Figure
1 – Chest X-Ray with a Right Tension Pneumothorax
2. Spontaneous simple pneumothorax
a. Collapsed lung caused by the rupture of a congenitally weak area on the surface of the lung.
b. Spontaneous simple pneumothorax’s usually occur in young white males, age 16 to 25 years old, who possess a very lanky, thin, runner’s build.
c. Symptoms usually occur when:
1. The patient is at rest and feels a popping sensation within the chest
2. The patient wakes up in the morning and feels short of breath
d. Spontaneous simple pneumothorax’s occur without evidence of trauma.
e. Signs and Symptoms:
1. Chest pain on the affected side
2. Dyspnea / Shortness of Breath
3. Symptoms usually begin during rest or sleep
4. Small pneumothorax:
a) Mild to moderate increase in respiratory rate
b) Mild to moderate tachycardia
c) Diminished breath sounds on affected side
5. Large pneumothorax:
a) Tachypnea – marked
b) Tachycardia – marked
c) Cyanosis
d) Absent breath sounds on affected side
e) Decreasing level of consciousness
C. NEEDLE THORACENTESIS
1. DEFINITION - A procedure where a needle and catheter are inserted through the chest wall and into the pleural space. The catheter provides a conduit for the release of accumulated pressure within the pleural space.
2. INDICATIONS FOR A NEEDLE THORACENTESIS:
a. Tension Pneumothorax
b. Simple pneumothorax (if the conditions become severe)
3. COMPLICATIONS ASSOCIATED WITH A NEEDLE THORACENTESIS:
a. Hemothorax - blood within the pleural space.
1) Caused when the needle punctures any vessels within the chest wall
b. Bacterial infection
1) Caused by poor aseptic technique
c. Subcutaneous emphysema – released air becomes trapped within the subcutaneous tissue. Feels like “rice crispies” underneath the skin.
d. Air embolism
1) Caused when the needle enters a great vessel within the chest wall and air is accidently introduced into the central circulation.
4. ANATOMY:

a. Mid-clavicular line b. Sternum c. Jugular Notch d. 2nd Intercostal Space e. Second Rib f. Clavicle
|
 |
 |
C. REQUIRED EQUIPMENT FOR
NEEDLE THORACENTESIS
1. 1 - surgical glove
2. Improvised flapper valve:
a. Remove one finger from the surgical glove
b. Place surgical glove finger over a 10-16g IV Angiocath with 3-10cc syringe
c. Place a small amount of water soluble lubricant at opening of surgical glove finger.
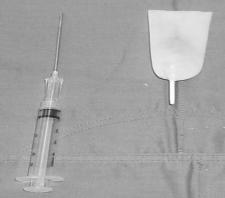
Figure 3 – Improvised Flapper Valve
3. 10-16g IV catheter with 3-10cc syringe attached
4. 1 Pair scissors
5. Betadine or Iodine
6. Dressing materials:
a) Sterile 2x2’s
b) Tape
D.
PROCEDURAL STEPS FOR NEEDLE THORACENTESIS
1. Position the patient – supine.
2. Identify the jugular notch, and the mid-clavicular line on the affected side of patient
3. Identify the 2nd intercostal space:
a. The 2nd intercostal space is found by dividing the clavicle in half. From that halfway point, palpate down one rib to the first space below that rib. This is the 2nd intercostal space (the space immediately after the clavicle is the 1st intercostal space).
4. Cleanse the site with betadine or alcohol (whichever is available)
5. Attach a 10-16 gauge IV catheter two to four inches in length snugly to a three to ten cc syringe. Attach flapper valve.
6. Insert needle into 2nd intercostal space.
7. Clear debris from the needle with air.
8. Remove needle and syringe, leaving the catheter and flapper valve in place.
9. Apply a small dressing around the catheter.
10. Place the patient in upright position (if C-spine injuries have been ruled out) to assist with respirations. The patient may remain supine if C-spine injuries are suspected.
11. Monitor the patients response to the needle thoracentesis
a. Respiratory rate
b. Lung sounds
c. The patient’s color
12. Continue to monitor the patient and reassess as necessary.
E.
UPRIGHT POSITION
1. Needle thoracentesis may also be performed with the patient in the upright position. All procedures are performed in the exact same manner as a patient in the supine position, except:
a. Insert the needle into the skin and direct the needle over the 3rd rib into the 2nd intercostal space (angled toward the head) and puncture the parietal pleura.
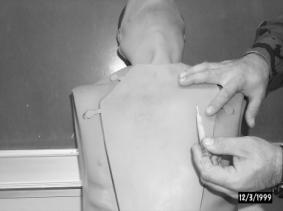
Figure 5 – Insertion of the Catheter in an Upright Patient
F.
SUPINE POSITION
1. Insert needle at a 90 degree angle into the skin and through the 2nd intercostal space and
puncture the parietal pleura, clear debris with air.

Figure 6 – Dressing Technique for Needle Thoracentesis
NOTE: If flapper valve stops functioning check for:
a. Resolved pneumothorax
1) Listen for return of lung sounds in all fields
b. Catheter is clotted
1) Place a 3 cc syringe on the end of the catheter. Gently pull back on the plunger to aspirate any material clogging the catheter.
REFERENCE
(S):
1. Emergency War Surgery
2. Pre-hospital Trauma Life Support
3. US Army Special Forces Medical Handbook (ST 31-9113)
4. Management of Wilderness and Environmental Emergencies
5. Advanced Trauma Life Support
Field Medical Service School
Camp Pendleton, California